Explain Different Fields of Udp Datagram
It is 16 bits. Here the connectionless service may.

User Datagram Protocol Udp Article Khan Academy
Length This field describes the total length of the UDP datagram including both data and header Information.
. UDP network traffic is organized in the form of datagrams which comprise one message units. One other important protocol in the TCPIP site is User Datagram Protocol UDPThis protocol is basically a scaled-down version of TCP. UDP User Datagram Protocol is a connectionless protocol of the internet protocol family that operates at the transport layer and was specified in 1980 in RFC Request for Comments 768.
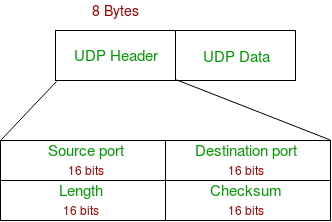
Just like TCP this protocol provides delivery of data between applications running on hosts on a TCPIP network but it does not sequence the data and does not care about the order in which the segments arrive at the destination. User Datagram UDP packets are called as user datagrams which contain the fixed-size header of 8-bytes. To explain the format of a UDP packet and discuss the use of each field in the header.
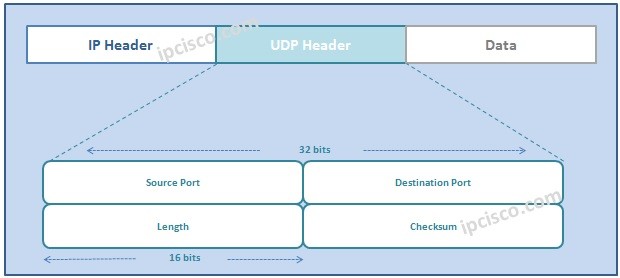
Figure 141 shows the relationship of the User Datagram Protocol UDP to the other protocols and layers of the TCPIP protocol suite. 1 User Datagram Protocol UDP is a connectionless protocol which means UDP is not a reliable protocol when compared with Transmission Control Protocol TCP. They are the following.
UDP packets user datagram has a fixed size header of 8 bytes. A 16 bits checksum. UDP is located.
2 Destination port number. Port number 0 is reserved. No frills bare bones extension of best-effort IP best effort service UDP segments may be.
Port numbers help to distinguish different user requests or processes. Source Port Number is 16 bits long. Source Port This is the port number of the application that is originating the user data.
The first 8 bytes of a datagram contain necessary header information and the remaining part consists of data. This field is used to detect errors over the entire user datagram header plus data. There is another field in the IP datagram that defines the length of the header.
The data section follows the header and is the payload data carried for the application. Checksum - This field stores the checksum value generated by the sender before sending. It is used by the process which is running on the source host.
The fields for UDP port numbers are 16 bits long giving them a range that goes from 0 up to 65535. UDP is located. Destination Port This is the port number pertaining to the destination application.
Length the length of the UDP header and data. UDP Header It is an 8-bytes fixed header. So UDP length IP length - IP headers length.
The fields are as follows. Following are the important characteristics of UDP. Source Port is a 2 Byte long field used to identify the port number of the source.
There is a field in the IP datagram that defines the total length. No handshaking between UDP sender and receiver each UDP segment handled independently of. To explain the format of a UDP packet and discuss the use of.
UDP User Datagram Format. The value sent for the checksum field is all 0s to show that the checksum is not calculated. The use of the checksum and source port fields is optional in IPv4 pink background in table.
Source port the port number of the application on the host sending the data. The first eight bytes of a datagram contain header information while the remaining bytes contain message data. IPv4 has this field as optional so when checksum field does not contain any value it is made 0 and all its bits are set to zero.
A UDP datagram header contains four fields of two bytes each. Port numbers help to distinguish different user requests or. This is the port number used by the process running on the source host.
The header consists of a 16-bit source port a 16-bit destination port a 16-bit length and a 16-bit checksum. The UDP datagram header consists of 4 fields each of which is 2 bytes 16 bits. A 16 bits destination port.
It is 16-bit information that identifies which port is going t send the packet. The UDP header contains four fields. Length the length in bytes of the UDP header and any encapsulated data.
It is 16-bits field and minimum value is 8-byte ie. User Datagram Protocol UDP UDP service. The UDP header is 8 bytes long and consists of the following fields.
It identifies which port is going to accept the information. The size of UDP header itself. 1 Source port number.
2 User Datagram Protocol UDP is capable of performing fundamental error checking. Destination port the port number of the application on the host receiving the data. When the sender complements the.
This is the port number used by the process running on the destination host. The User Datagram Protocol header has four fields each of which is 2 bytes. This is a.
A UDP datagram consists of a datagram header and a data section. As a lean and almost delay-free alternative to TCP UDP is used for the fast transmission of data packets in IP networks. Source port number which is the number of the sender.
A 16 bits length field. As the port numbers are encoded as a 16 bits field there can be up to only 65535 different server processes that are bound to a different UDP port at the same time on a. Datagram Protocol UDP to the other protocols and layers of the TCPIP protocol suite.
Destination port number the port to which the datagram is addressed. UDP port number fields are each 16-bits or 2-bytes long. Lost delivered out of order to app connectionless.
UDP port number fields are each 16 bits long therefore the range for port numbers is defined from 0 to 65535. The important fields of user datagrams are. This is the information used to send the datagram toward its destination.

No comments for "Explain Different Fields of Udp Datagram"
Post a Comment